[ad_1]
Flour is a staple ingredient in lots of baked items, however not all flours are created equal. Listed here are some various kinds of flour, the dietary data for every, and the right way to incorporate these flours right into a wholesome meal plan.
OnPoint Vitamin has helped greater than 3,000 shoppers with distinctive well being hurdles, and a whole bunch of them particularly with balancing diet and constructing a more healthy relationship with meals.
At OnPoint Vitamin, we perceive that this could be a tough and prolonged expertise, however you aren’t alone. We now have helped a whole bunch of shoppers with related challenges to develop a more healthy way of life.
On this article we’ll go over the various kinds of flours, greatest use and a number of the dietary advantages as a way to take advantage of knowledgeable selections on your greatest well being.
Varieties of Fours
Flour is a finely-ground, sifted meal of grains, nuts, seeds, legumes or sure greens.
Discovering the fitting flour will be important for a lot of causes, particularly for folks with particular dietary wants or preferences. As an illustration, these with celiac illness or gluten intolerance should keep away from wheat flour and different gluten-containing flours to keep away from antagonistic well being results.
Moreover, some folks may have to watch their carbohydrate consumption and select flours with decrease carbohydrate content material, reminiscent of almond flour or coconut flour.
Moreover, completely different flours have distinctive flavors and textures that will improve the style and high quality of particular dishes. For instance, chickpea flour might add a nutty taste and dense texture to baked items, whereas rice flour might create a lighter, fluffier texture.
Thus, discovering the fitting flour can considerably influence the style, texture, and dietary worth of assorted meals, making it a vital consideration for anybody trying to optimize their weight-reduction plan and well being.
The next is an in depth description of the various kinds of flour and their diet profiles and cooking/baking qualities:
Wheat Flours
Wheat flours are probably the most prevalent and are historically milled. Refined wheat flours are enriched with thiamin, riboflavin, niacin and iron, and fortified with folic acid by legislation. Complete-wheat flours, which naturally comprise B nutritional vitamins and iron, along with selenium, potassium and magnesium, are good sources of fiber. Nevertheless, whole-wheat flours will not be enriched with folic acid.
The wheat flour class alone is intensive. Flours from “arduous” wheat are perfect for bread making, as they’re increased in protein (together with gluten), which makes dough sticky, elastic and in a position to maintain air bubbles fashioned by a leavening agent because the dough rises. Flours from “comfortable” wheat have much less protein and fewer elastic high quality, so they’re higher for delicate pastries and desserts.
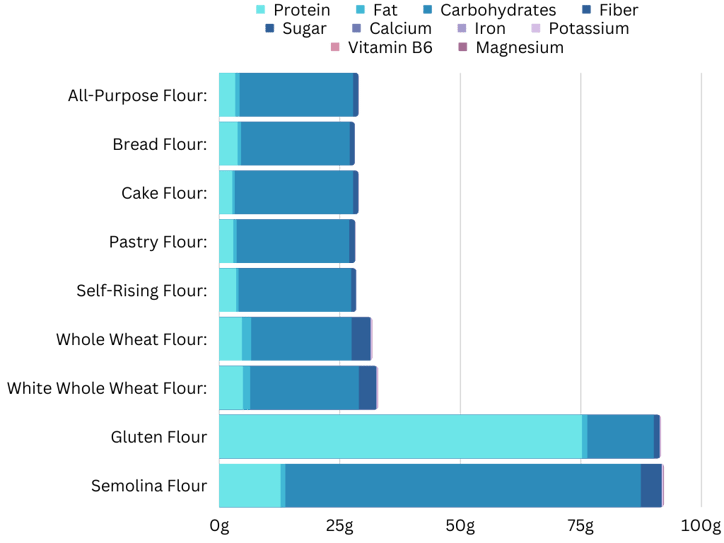
1. All-purpose flour
It is a refined mix of high-gluten arduous wheat and low-gluten comfortable wheat. It’s milled with solely the endosperm (not bran or germ) and is used for baking, thickening and breading. It’s normally bought pre-sifted and is typically fortified with calcium and nutritional vitamins A or D.
All-Function Flour:
- Protein: 3.3g
- Fats: 0.9g
- Carbohydrates: 23.5g
- Fiber: 0.9g
- Sugar: 0.2g
- Calcium: 0.003g
- Iron: 0.0014g
- Potassium: 0.036g
- Vitamin B6: 0.00003g
- Magnesium: 0.004g
2. 100% whole-wheat flour
That is comprised of hulled pink wheat grain (wheat berries). It supplies extra fiber and different vitamins and is used instead of all-purpose flour. It makes a heavier bread, and in baked items, it’s usually combined with all-purpose flour for a lighter texture and higher rising. It has a shorter shelf life than all-purpose flour.
Complete Wheat Flour:
- Protein: 4.7g
- Fats: 1.9g
- Carbohydrates: 20.8g
- Fiber: 3.5g
- Sugar: 0.4g
- Calcium: 0.034g
- Iron: 0.0015g
- Potassium: 0.287g
- Vitamin B6: 0.00026g
- Magnesium: 0.054g
3. White whole-wheat flour
That is comprised of hulled white spring wheat. It may be used as an alternative of normal whole-wheat flour in baked items for a milder style and lightweight colour.
White Complete Wheat Flour:
- Protein: 4.9g
- Fats: 1.5g
- Carbohydrates: 22.5g
- Fiber: 3.2g
- Sugar: 0.4g
- Calcium: 0.028g
- Iron: 0.0014g
- Potassium: 0.308g
- Vitamin B6: 0.0002g
- Magnesium: 0.054g
4. Self-rising flour
That is all-purpose flour with added salt and baking soda. It’s a comfort product not typically used for yeast breads. The leavening motion of baking soda can diminish if saved too lengthy.
Self-Rising Flour:
- Protein: 3.5g
- Fats: 0.5g
- Carbohydrates: 23.3g
- Fiber: 0.8g
- Sugar: 0.2g
- Calcium: 0.004g
- Iron: 0.0012g
- Potassium: 0.036g
- Vitamin B6: 0.00004g
- Magnesium: 0.004g
5. Cake or pastry flour
It is a fine-textured refined flour comprised of comfortable wheat. It’s excessive in starch and used for tender desserts and pastries.
Cake Flour:
- Protein: 2.7g
- Fats: 0.5g
- Carbohydrates: 24.5g
- Fiber: 0.5g
- Sugar: 0.6g
- Calcium: 0.003g
- Iron: 0.0008g
- Potassium: 0.028g
- Vitamin B6: 0.00003g
- Magnesium: 0.003g
Pastry Flour:
- Protein: 2.9g
- Fats: 0.7g
- Carbohydrates: 23.3g
- Fiber: 0.9g
- Sugar: 0.3g
- Calcium: 0.003g
- Iron: 0.0012g
- Potassium: 0.032g
- Vitamin B6: 0.00003g
- Magnesium: 0.005g
6. Bread flour
It is a refined flour comprised of arduous wheat and a small quantity of barley flour. It has very excessive gluten content material and is used for bread making.
Bread Flour:
- Protein: 3.8g
- Fats: 0.7g
- Carbohydrates: 22.5g
- Fiber: 0.8g
- Sugar: 0.2g
- Calcium: 0.009g
- Iron: 0.0015g
- Potassium: 0.039g
- Vitamin B6: 0.00004g
- Magnesium: 0.007g
7. Gluten flour
It is a refined flour comprised of arduous wheat with most starch eliminated. It has a considerably increased protein (gluten) content material than all-purpose flour, which will increase the power and rising energy of dough. It’s blended with lower-gluten flours for bread.
Gluten Flour:
- Protein: 75.2g
- Fats: 1.1g
- Carbohydrates: 13.8g
- Fiber: 0.8g
- Sugar: 0.4g
- Calcium: 0.01g
- Iron: 0.007mg
- Potassium: 0.22g
- Vitamin B6: 0.002mg
- Magnesium: 0.032g
8. Semolina flour
That is typically coarsely-milled, refined arduous durum wheat flour. It’s used for pasta, couscous, gnocchi, and puddings. It’s excessive in gluten. Coarsely-milled different wheat grains may be referred to as semolina, reminiscent of corn semolina (grits) and rice semolina.
Semolina Flour:
- Protein: 12.7g
- Fats: 1g
- Carbohydrates: 73.7g
- Fiber: 3.9g
- Sugar: 0.4g
- Calcium: 0.024g
- Iron: 0.004mg
- Potassium: 0.338g
- Vitamin B6: 0.16mg
- Magnesium: 0.138g
Non-Wheat Flours
Non-wheat flours are an ideal possibility for individuals who comply with a gluten-free weight-reduction plan or for many who need to experiment with completely different flavors and textures.
These flours are normally comprised of grains, nuts, seeds, or legumes and supply quite a lot of makes use of and qualities.
Correct storage is crucial to extend their shelf life since most of them are bought in pre-packaged portions.
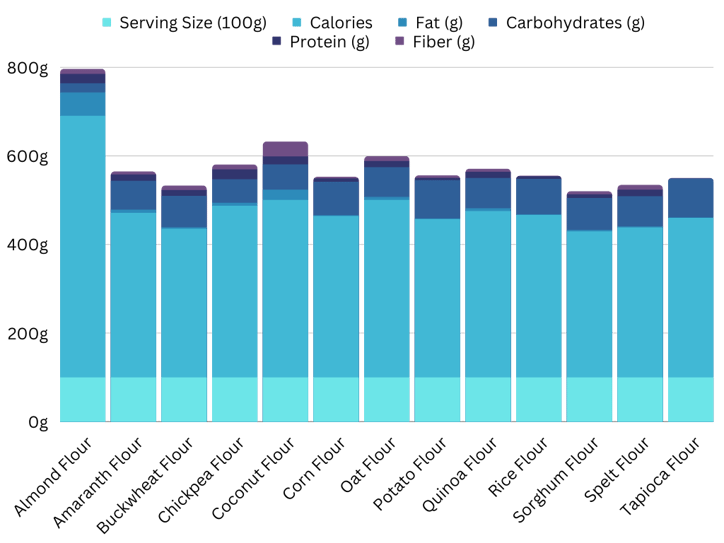
Chart: Serving dimension (100 grams), Widespread Non-Wheat Flour
Listed here are some well-liked non-wheat flours and the right way to use them:
1. Almond meal/flour
Produced from blanched almonds, it’s low in carbohydrates and excessive in protein. In ¼ cup, it accommodates 6g of protein, 3.5g of fiber, 60mg of calcium, 10 IU vitamin E (35% Every day Worth), and 14g of fats, almost all unsaturated. It provides moisture and nutty style to pastries, baked items, and dessert fillings. Nevertheless, it isn’t meant to exchange flour in yeast or fast breads. It has a brief shelf life and must be refrigerated or frozen in hermetic containers to retain its powdery high quality.
Almond flour:
- Energy: 163 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 14g
- Carbohydrates: 6g
- Fiber: 3g
- Protein: 6g
2. Chickpea Flour:
Produced from floor chickpeas, this flour is excessive in protein and fiber. It is generally utilized in Indian and Center Japanese delicacies to make dishes like pakoras, socca, and falafel.
Chickpea flour:
- Energy: 356 per 1 cup
- Fats: 6g
- Carbohydrates: 53g
- Fiber: 10g
- Protein: 21g
3. Coconut Flour:
Produced from floor coconut meat, this flour is excessive in fiber and low in carbs. It is generally utilized in gluten-free baking, and can be utilized to make pancakes, desserts, and breads.
Coconut flour:
- Energy: 120 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 4g
- Carbohydrates: 16g
- Fiber: 10g
- Protein: 4g
4. Buckwheat flour
Produced from buckwheat, which is a cousin of rhubarb (not a wheat varietal nor technically a grain). It’s normally mixed with different flours so as to add a hearty, grassy taste and colour to bread. It’s good for pasta and pancakes. Complete buckwheat flour has a stronger taste and extra vitamins, whereas white buckwheat is milder and has fewer vitamins.
Buckwheat flour:
- Energy: 92 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 1g
- Carbohydrates: 20g
- Fiber: 3g
- Protein: 3g
5. Corn flour
Milled from the entire corn kernel (cornstarch is comprised of the endosperm). It’s utilized in breading or blended with different flour for batter or dough. Be aware that cornmeal will be floor into corn flour in a meals processor.
Cornmeal:
- Energy: 104 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 1g
- Carbohydrates: 22g
- Fiber: 2g
- Protein: 2g
6. Hazelnut Flour:
Produced from floor hazelnuts, this flour is excessive in wholesome fat, protein, and vitamin E. It is nice for gluten-free baking, and can be utilized to make desserts, cookies, and muffins.
Hazelnut flour:
- Energy: 170 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 14g
- Carbohydrates: 8g
- Fiber: 4g
- Protein: 5g
7. Oat flour
Floor from oat groats, it’s used to exchange some flour in quite a lot of recipes. It provides a wealthy, nutty taste and denser texture. In baked meals that have to rise, it have to be mixed with different flours.
Oat flour:
- Energy: 104 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 2g
- Carbohydrates: 18g
- Fiber: 3g
- Protein: 4g
8. Sorghum Flour
Produced from floor sorghum, this flour is excessive in protein and fiber. It has a barely candy taste, and is usually utilized in gluten-free baking.
- Energy: 120 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 1g
- Carbohydrates: 25g
- Fiber: 3g
- Protein: 4g
9. Potato flour
Floor from entire, dried potatoes, it accommodates 2.5g of fiber and 400mg of potassium (12% DV) in ¼ cup. It’s used as a thickener for clean, creamy sauces, soups, gravies, and frozen desserts. For baking, it provides starch to the dough, which attracts and holds water and makes bread extra moist, extending
Potato flour:
- Energy: 120 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 0g
- Carbohydrates: 27g
- Fiber: 2g
- Protein: 2g
10. Brown & White rice flour
Produced from unpolished brown rice, brown rice flour has a nutty taste and a grittier texture than white rice flour. In 1/4 cup, brown rice flour accommodates 2g of fiber, in comparison with 1g in white rice flour. Brown rice flour is gluten-free and whole-grain, making it an ideal possibility for these with celiac illness or in search of a nutrient-dense different to white flour. It may be used like white flour in recipes, however might require extra liquid resulting from its denser texture. Attempt utilizing brown rice flour in recipes like cornbread and pound cake for a nutty twist on traditional baked items.
Produced from white rice, white rice flour is usually utilized in baked items like pie crusts and cookies. In shortbread, it offers a young mouthfeel. Candy or glutinous “sticky” rice flour is comprised of high-starch, quick grain rice, which is used to thicken sauces in Asian dishes. Regardless of its identify, glutinous rice flour doesn’t comprise gluten and can also be gluten-free. It is a good possibility for many who are gluten illiberal or have celiac illness. Whereas not as nutrient-dense as brown rice flour, white rice flour can be utilized as an alternative to wheat flour in lots of recipes.
Rice flour:
- Energy: 130 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 0.5g
- Carbohydrates: 28g
- Fiber: 1g
- Protein: 2g
11. Tapioca flour
Produced from cassava root, this flour is excessive in carbs and low in protein. It is generally used as a thickener for soups and stews, and will also be utilized in gluten-free baking.
Tapioca flour:
- Energy: 100 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 0g
- Carbohydrates: 26g
- Fiber: 0g
- Protein: 0g
12. Soy flour
Produced from milled soybeans, soy flour is excessive in protein and decrease in carbohydrates than all-purpose flour. In 1/4 cup, soy flour accommodates 10g of protein, 8g of whole carbohydrate, and 3g of fiber. It’s a good supply of calcium and a very good supply of iron and magnesium. Soy flour can be utilized to thicken sauces and as a wheat flour substitute in fast breads and cookies, the place 1 half soy flour will be substituted with 3 elements all-purpose flour. It additionally reduces fats absorption in frying batter or dough. Calmly toasting soy flour in a dry skillet over reasonable warmth can add a nutty taste to baked items.
Soy flour:
- Energy: 105 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 1g
- Carbohydrates: 9g
- Fiber: 6g
- Protein: 13g
13. Spelt flour
Produced from spelt, an historic grain and cousin to wheat, spelt flour is barely increased in protein and gluten than wheat flour. In 1/4 cup, spelt flour accommodates 4g of protein, 4g of fiber, and 1.5g of iron (8% DV). It has a mellow, nutty taste and will be substituted for wheat flour in baking. Nevertheless, it might trigger reactions in these with wheat allergic reactions. Each refined and entire spelt flour can be found. Complete spelt flour is a whole-grain possibility that provides texture and taste to baked items.
Spelt flour:
- Energy: 120 per 1/4 cup
- Fats: 1g
- Carbohydrates: 24g
- Fiber: 4g
- Protein: 5g
Incorporating these flours right into a considerate meal plan can present quite a lot of vitamins whereas additionally catering to dietary wants. For instance, utilizing brown rice flour in a gluten-free recipe or incorporating soy flour right into a excessive
How Can An On-line Dietitian Assist Me Select the Proper Flour For My Food plan Plan?
A registered dietitian can play a crucial role in serving to you select the fitting flour on your dietary wants and meal plan. They’ll present steerage on the right way to choose flours that align along with your particular well being objectives and dietary restrictions.
For instance, when you have celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, a dietitian can assist you establish gluten-free flours that can be utilized as substitutes in your favourite recipes. They’ll additionally enable you to navigate the varied flour alternate options that exist for these following a low-carbohydrate or low-FODMAP weight-reduction plan.
As well as, a dietitian can help you plan balanced meals that incorporate the fitting varieties and quantities of flours. They’ll present schooling on the nutrient composition of various flours and enable you to make knowledgeable choices about which flours to make use of for sure recipes or meals.
As an illustration, a dietitian can recommend utilizing entire grain flours for elevated fiber content material and to slow the release of glucose into the bloodstream, which can assist regulate blood sugar ranges. That is helpful to these battling prediabetes/diabetes.
The identical organic ideas will be utilized to many situations of well being and it’s all the time greatest to incorporate knowledgeable in a well being plan when coping with a power sickness.
General, consulting with a registered dietitian will be a useful useful resource in serving to you select flours that align along with your dietary wants and preferences whereas nonetheless offering the style and texture you want in your meals.
Taking the Subsequent Steps
Selecting the best elements to construct a wholesome diet plan could be a daunting activity, particularly in the case of flour varieties. At OnPoint Vitamin, we perceive the significance of a nutritious and personalised meal plan, and that is why we provide the help of our group of professional dietitians.
Our registered dietitians will educate and information you on choosing the proper flour varieties that suit your dietary wants and meal plan. We acknowledge that there are quite a few choices out there out there, and it may be overwhelming to find out your best option.
We take a personalized approach to develop a constant and sustainable plan for achievement in cultivating a meal plan that satisfies and nourishes your physique. This method will domesticate a wholesome and balanced relationship with meals, permitting you to construct a meal plan that’s each nutritious and satisfying.
We hold up-to-date with the newest analysis and modify our method based mostly on validated medical investigations, making certain that you just obtain the best and personalised steerage.
Our online team of registered dietitians and Nutritionists is accessible to help you in your journey in direction of a more healthy and extra fulfilling life. With the assistance of our group , you possibly can acquire the data and instruments wanted to make knowledgeable selections about your diet.
Empower your self to attain higher well being with OnPoint Vitamin.
Contact us to start out constructing a more healthy meal plan at this time!
[ad_2]

